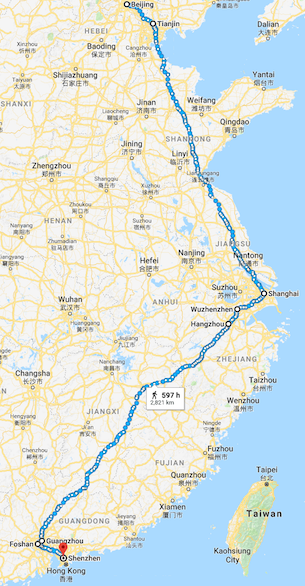
24 days exploring China
The last 24 days I’ve been wandering around different cities in China. My plan was to not have a plan. For once I wanted to travel alone and spend some time in different cities combining casual sightseeing, meeting people and making friends as diverse as possible. I wanted to talk, listen to people’s stories, lives, woes, concerns and successes. I wanted to meet businesses and entrepreneurs as well, also some potential suppliers for Camaloon. I was in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Wuzhen, Hangzhou, Guangzhou, Foshan, Shenzhen and finally Hong Kong.
My first realization was that I should have made this trip years ago. China takes a big part in our contemporary world, it has many resources and lots, lots of people. One cannot simply stay out of it and pretend to be globally oriented as I do!
Following you can read my personal impressions and experiences on my trip.
Communication, my biggest issue
Language has been my biggest issue. I don’t talk Chinese and I realized the learning curve is so steep, even for the most basic words and sentences. Still, I have not given up yet. Translation apps, such as Google Translate, Microsoft translate and others made my life easier.
Chinese has completely different phonetics, 5 or 6 tones (Mandarin/Cantonese), their language is based on the combination of abstract ideas, where order and context matters a lot. Their writing is made up of thousands of symbols people memorize and combine (well, since the simplification Mao Zedong made on 1952 there are “only” 8.500 more simple characters compared to traditional writing). They have lots of sublanguages (some people call them dialects) but they share one unique writing.
Chinese people now start to learn English at school when they are 3 years old and they take it very seriously, English schools and academies are a huge industry and I met many people making a living directly or indirectly from it. That makes the typical entrance for foreigners, as there is a big shortage of native teachers almost everywhere.
However, most people I found could not say a word in English, they either were too shy to try, some just ran away, others looked for colleagues around who finally couldn’t say anything either. I’m not talking about isolated cases but that was the story of most of my street encounters with random people in mainland China.
However, people are open-minded, extremely hospitable, fun and have a great sense of humor. They are curious, and find interest in exchanging ideas and conversation with foreigners. Some locals who went abroad and came back complain that Chinese spoil foreigners too much (which differs from the discrimination they suffered when they lived in western countries).
In many aspects I felt closer to Chinese than to other European neighbors who are more rational, serious and formal.
Urbanization, world’s greatest migration
The greatest migration movement that has ever taken place in our planet is that of over 500 million Chinese relocating from the countryside to the metropolis since the early 80’s until today. As birth rate in the countryside keeps being substantially higher than in cities, this movement will keep on for long.
All these newcomers to the cities share similar characteristics: They start from scratch in a highly paced environment, with lots of expectations and pressure, very few friends or known people and they have the mandate to learn, build a great career, make money, find wife/husband and come back every Spring for the Chinese New Year to show progress to their families. Almost 200 million people move every Spring to their hometowns.
Europe has a long tradition of migrations, and yet the magnitude of people who ever moved in or out ranges around 100 times lower than that of China.
Most people I met, specially young ones, felt lonely and paradoxically developed even stronger ties to their far away parents with whom they chat on Wechat everyday. For this reason I believe family life far from being weakened, it might have strengthened.
Family and marriage are central
Family is probably the pillar in people’s life. Not a single person has not raised the issue of “what my parents want or say” even in our first conversations. The parents wills and desires are so strong in their children’s mind (even if they constantly complain about it) that sometimes can become overwhelming. For most young people I met, the top influencer was the mother, who generally is in charge of the child’s growth and education while the father spends more time out making money.
Parents will be taken care of by the child when they retire, so kids need to produce enough wealth on their careers and marriage. Either parents will eventually move to the cities, or their sons and daughters will return to their hometowns. Thus, marriage is key. It almost feels like the musical chairs, where everybody is looking for the perfect husband/wife (sometimes in purely economic sense) that will suit their parents.
This extremely materialistic approach (I hardly ever saw parents concerned about their children’s dreams or life vocation) probably comes from the very tough times that China experienced during Mao’s Cultural Revolution. In that time, where most kinds of businesses/trade were banned (among other things), many people actually starved to death. Some people told me the stories of how they were forced to eat tree roots to survive at that time.
Fortunately, that changed later on with Den Xiaoping’s reforms and it was the beginning of an aggressive planned capitalism that would transform society, first make people produce and save, and later push them to get trained and spend.

Officialism and collective influence
Compared to Europe, Chinese feel extremely comfortable with the establishment. They also follow patterns and trends like I’ve seen nowhere else. Except for the people in Hong Kong (who I found to be quite diverse), I could notice little differences between how people dressed, their styles, things they do and own, … Many people travel in groups, follow government rules, they get their info from the same censored media outlets and propaganda. And that’s ok. Most people do not have a VPN to access the outside world. Some don’t know about it, others say they don’t need it.
Me asking if they have ever thought of a different political or economical system for their country the unison answer is: no, why should they? When asking about controversial things being perpetuated by their government, most people either don’t know/believe them, or say that was long ago, or simply say that still makes the best option for them at the moment.
That is possibly one of the biggest differences with European civil society. To some extent people abandon individual ideas in pro of the collective. On the opposite side, European youth obsesses with indie, underground or bohemian movements all the time, as a trend itself.
Consumerism goes crazy
If there is one thing I observed Chinese like, that is buying. They have malls everywhere, shops, street food bars, tea shops, restaurants, KTVs (individual karaokes), all kinds of attractions. Most people I met never cook at home, instead they order food or eat out.
Some people have one or two cell phones (most of them are iPhone) from which they continuously buy lots of things in Taobao or Meituan. Sometimes as we were having a conversation, they would feel hungry and order fruit or anything online (it didn’t matter it was Saturday almost midnight) and a delivery man would show up after 30 minutes with the items they ordered. They delivered to us all kinds of things at all kinds of places at a record speed.
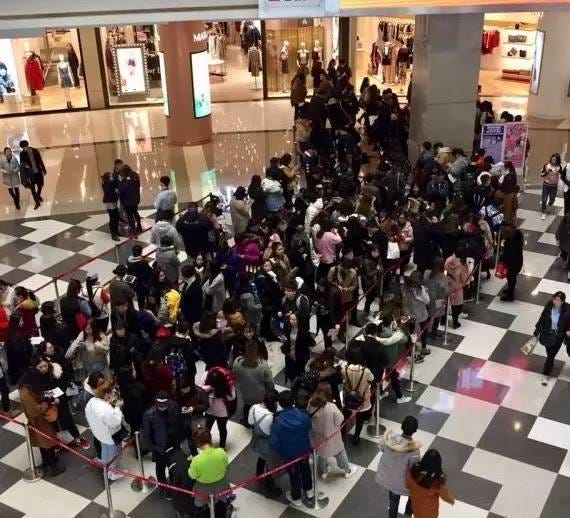
Fast pace, multitasking and brute force
The pace is so fast that you would not believe it until you experience it. People walk everywhere in huge crowds, almost not leaving free space or a slow lane in the street or subway. Almost all the people are eating or using the phone while walking, so they expect the flow to be continuous. You always feel pushed (sometimes literally) by the person behind you to move faster and never ever stop. I guess I was a turtle for my Chinese friends who would always ask me to go “quickly!”.
The idea of letting people out from places before getting in seems an abnormality. I’ve seen real battles by old ladies trying to get out from the train by pushing bellies around them. The streets and roads in Beijing and Shanghai are the most chaotic (and funny at the same time) thing I’ve seen. People drive in all directions on any road: eScooters (200€ electric scooters most people own), bikes (mostly from the super cheap OFO and Mobike app services), rickshaws, cars, buses, pedestrians, they all share and meet at the same space. Everybody (ab)uses the horn by default, not expecting anything from it, just as part of their driving. I saw a few crashes, but as none was serious, no one even stopped, they continued driving like nothing happened. I drove an eScooter a few days in Beijing and I felt inside a videogame. Great fun.
When you pay attention to what people actually do on their phones, you see they do all sorts of things (at once!). People watch TV (mostly shows or films), play videogames, chat with many people (sometimes work related), buy things online, all at the same time at a record speed. They do that while commuting (sometimes driving a bike or motorbike), while eating and sometimes while talking to you (something I came to hate). I felt an old guy asking people to focus on one thing.
While I was observing people, I was thinking of how this very idea of multitasking portraits China’s society. They are capable of doing so many things (sometimes at once). It makes sense to think that sometimes, statistically, some things will make a lot of sense. So many people doing so many things must trigger some sort of combinatorial darwinism that will produce the right things, sometimes new things. I came to realize that this iterative process (programmers call it brute force) is in fact a viable process for innovation.
Economy and business enablement
If the official numbers are right we are in front of a highly populated (1,4B people) economy that grows at a 7% YoY (compared to the 1,6% of the US or 2,3% of EU).
Traditionally China comes from many centuries of a real autarchy (autonomous economy). They were able to produce all goods they needed in their vast and varied territory. It looks as if today 4 decades after their industrial revolution, they created enough middle class consumers so as to build their own huge internal consumer market again, which timely combined with a great consumerism appetite. Even in tourism, I could see how most visitors in all attractions and monuments were Chinese internal tourists.
Labor that used to be cheap and deregulated, it is now more expensive (around 500–600€ typical blue collar salary + 100–200€ insurance) and more closely regulated and controlled. Industrial production was once virtually free, and now is regulated and closely controlled by the government, leading to the closedown of many factories for environmental damage.
I could see so many government related job positions that seem to belong to a sort of country wide Keynesian policy. I found lots of people doing jobs of little importance (if not completely irrelevant). Such as traffic control, passport and security control, crowd organizers, door control everywhere and ticket offices at parks and all kinds of public spaces, etc.
I believe the main issues preventing more businesses from developing and foreign investment are legal uncertainty, kafkian bureaucracy, government opacity and corruption. Most foreign people who started companies there told me that the only chance to succeed is by having a partner who has ties with the government.
As I attended some entrepreneurship events, I could see a widely developing venture capital scene, corporate accelerators, venture builders, startup hubs and many entrepreneurs executing fast and strongly committed to get shit done.

Massively efficient infrastructure
I was surprised by how good most infrastructure works in China.
Even if it comes at the cost of privacy, you can always feel secure. Police is available everywhere, there are security cameras all over, even at the beach!
Public transportation is very modern, trains and buses come at very high frequency, the price is super cheap and the service is close to excellent.
Hospitals open 24 hours 7 days a week, you can book and even ask questions online.
Public toilets are available everywhere, they are clean and almost always have soap (but no tissues, you are supposed to bring it always with you).
Lots of taxis are available at a very low cost, sometimes even free (it was the case of some days in Shanghai). Competition is fierce and Didi (China’s Uber) lowered prices of the overall market. Everybody can drive a Didi, therefore everybody can afford taking it.
Bikes are available everywhere by two main companies: Mobike and OFO. They are so affordable and convenient that they replaced most people’s own bikes.
Internet and the great (fire)wall
There are two state owned competing telcom companies operating in China since 1994. Their coverage is so massive and good that I hardly ever lost my signal anywhere. I paid 15€/month for unlimited everything and high-speed internet connection, and it delivered as promised.
However, China’s Internet should be called an intranet (no matter how big) instead. All traffic is carefully controlled by the government and highly censored. The Internet as we know it doesn’t exist. I could not access any Google service (from Gmail, Maps, Google Translate), Slack, Facebook, Youtube, Twitter, Whatsapp had a terrible performance and no images or video, I couldn’t access most of global or Spanish newspapers, … at least without a decent VPN (which slowed down the connection, and continuously self-disconnected). I used Nord VPN.
Most people I saw of all ages used iPhones to connect to the Internet. That’s probably why China is the biggest market for Apple phone sales (though many people told me that it would decline as Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, Xiaomi and other Chinese manufacturers were getting much better). I also realized that iPhone’s price was even higher than in Spain, making it a big investment for the lower Chinese purchasing power. China has the biggest Internet connected population, 730 million people. Following are India (460M users), and US (290M users).
Baidu is what most people use for search, maps and most of Google equivalent services. It only works in Chinese, so I could not make much use of it.
Tencent’s Wechat is the answer to Whatsapp and Facebook combined, but it has many more features. For example, Wechat is used to pay for all kinds of things. Most people don’t carry cash anymore, as they can use Wechat absolutely everywhere. A street tyre fixer, a parking controller, or even a beggar have QR codes you can scan to pay them. I saw how grandmas sent Wechat money to their grandsons. Every time I started counting my cash to pay in a restaurant my friends had already split the bill, paid and were waiting for me outside… But Wechat is also replacing email, as they feel more comfortable with instant synchronous answers. Most businesses (sales or customer service) will give you their Wechat contact to communicate with them. Interestingly, Wechat has its own application store of HTML based “mini-programs” that can access user IDs and Payment solutions. I used Meituan and OFO inside Wechat.
What Tencent is to social, Alibaba is to b2b and b2c ecommerce. Taobao, Tmall.com, Alibaba.com are widely used to buy things online (along with JD.com and a few others).
Alipay is Alibaba’s electronic bank solution similar to Wechat’s. Both Tencent and Alibaba filed for bank licenses some years ago and are already operating as full-scale banks in the whole country. They offer b2c and b2b loans and have developed their own social reputation scoring systems that the government is considering to officialize as public reputation systems (yes, scary).
They say China’s Internet is oligopolistic and concentrated in few mega-apps mainly the BAT (Baidu, Alibaba and Tencent) conglomerates, and only recently being matched by the second group TMD (Toutiao, Meituan-Dianping and Didi Chuxing). Toutiao is the most popular news site in China, Meituan is the leader for last mile delivery services and food discovery, and Didi is the leader in mobility. All these companies are constantly innovating, copying western products and services, and buying companies that add up to their offering and their huge customer base.
Most entrepreneurs I talked to were in some way digging into big data, machine learning and all applications of artificial intelligence. As the number of connected users is so huge and such few services accumulate so much user data and trends, combined with some relaxed privacy laws, I bet there is no better greenfield for AI experimentation in the world. I’m excited and afraid in equal parts of what can be accomplished by China on this field.
Hong Kong is the western backdoor
After centuries of positive trade balance for China against western countries (as they had enough resources and goods and had little interest in foreign products), the British started exporting Indian grown opium to China creating millions of addicts and serious consequences for China’s economy. When the emperor stopped British ships from trading opium and banned it, Great Britain, and later France, declared war to China. They totally smashed their unsophisticated armies, killed many and destroyed historical enclaves. That resulted in a humiliating treaty that would give unequal trade rights to the British and others and would grant the island of Hong Kong to the British empire forever. It wasn’t until 1997 that the colony was given back to China on the condition that its system would remain unchanged for the 50 years to come. Hence ‘One Country, Two Systems’.
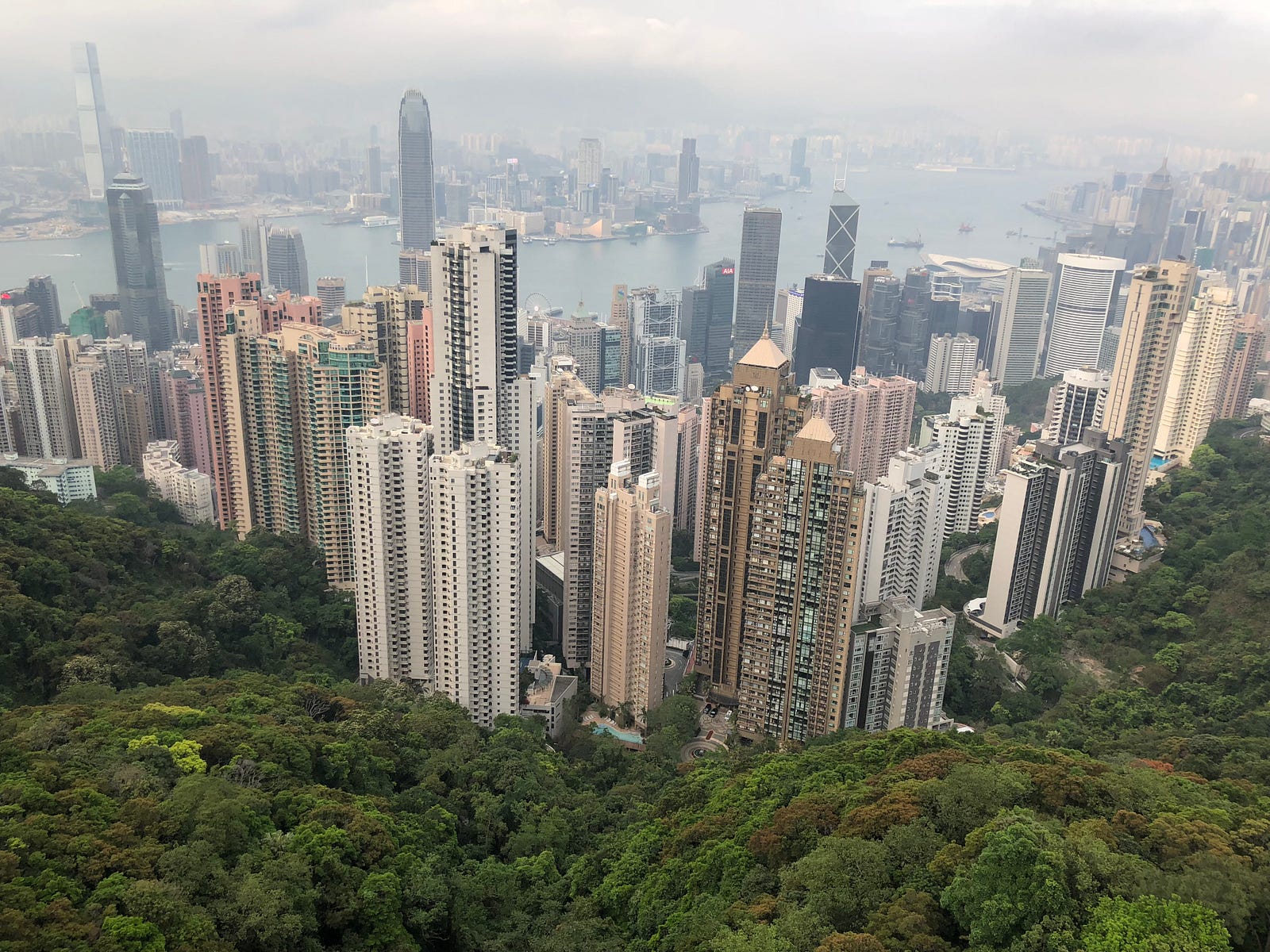

Today HK is a melting pot of people from every part of the world and a majority of Cantonese Chinese. Fast, dynamic, open, free of entry without Visa, free access to uncensored Internet, most ordered public spaces, British right hand side lanes and car wheels. Mainland Chinese and Hongkongers regard each other with disdain. Hongkongers consider themselves more educated and open. Mainland Chinese historically consider them as sellouts, traitors or foreigner collaborators. HK is a tax heaven, financial capital in Asia, and also the center of operations for many companies who trade with China mainland, specially in the neighbor area of Guangdong, where the most important Chinese business trade show takes place: the Canton fair. You can cross the border with China on foot, through a bridge. I could see that many people does it everyday for work.
In HK many people speak English, many foreigners live there and it is the first time I see such amount of luxurious cars everywhere in the street. So many Tesla cars! A guy told me that around 15% of the inhabitants are millionaires. Of course the rest resign to live in the smallest apartments I’ve ever seen: smaller spaces than a parking spot where they’ve got kitchen, toilet and a room that sometimes share with different people.
Most things are very expensive, specially compared to China mainland. Transport is very efficient, some people never see sunlight as both their work and home buildings have direct access to subway. The subway card called Octopus also allows you to access and pay in most places from restaurants to supermarkets. An intricate net of tunnels and bridges allows you to cross the city without ever stepping a foot on the ground. Public and private spaces mix together: You go up some stairs to take a bridge, that later becomes a corridor, then it brings you to a bank hall, then a mall, then a roof park. It makes a very strange concept of urban space, that can become a challenge for orientation for people like me.
Conclusion and last thoughts
A country that has planned to lead the world and is committed to do so with an army of 1,4B productive workers (before blue collar and now highly trained) and consumers who are extremely pressured to learn and innovate, Europeans should feel called to work harder, to differentiate and join forces with them. We need more critical, strategic and creative thinking so as to compete and use more efficiently our smaller resources.
As competition gets more and more fierce, only powerful brands and very innovative concepts stand some chance against the oligopolistic conglomerates of the Chinese market. They have solutions (online products and services) for virtually everything: from cloud infrastructure, financial and human resources management, printing, mobility, … you name it.
We should waste no time and start placing China in our roadmaps!
You can check the pictures I took on my instagram. Check also Itnig podcast 27, where my friend Alexis Roig explains his experience running companies in China.